Reformatting Export Text for Compatible Imports
When you import applicant names from Outcomes into another system, there may be compatibility issues due to special characters, accent marks, excessive length, whitespace variations, or other unsupported formatting. From this article, you'll learn how to use JavaScript expressions in your exports to modify names in your exports as follows:
- remove special characters
- replace accented characters
- correct the letter cases
- set a character limit
To accomplish these things, you'll combine various code snippets to achieve the desired output.
Setting Up the Export
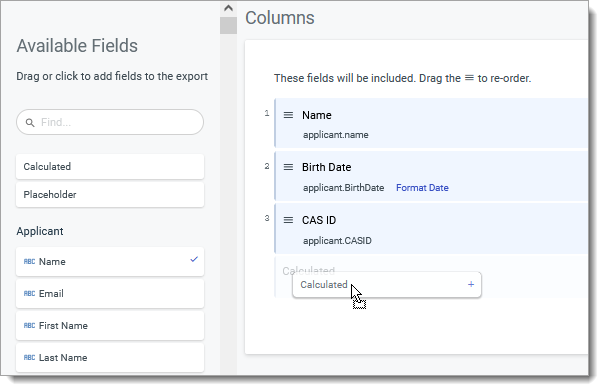
To complete this configuration, you'll need to add a Calculated Field to a Tabular/Spreadsheet Export. You can do this while configuring your Export by dragging a Calculated Field into the Columns to export.
After dropping in the Calculated Field, use the JavaScript Expressions option by clicking the function icon and dropping the code listed below into the Expression field.
Then, update the code to indicate which field you are exporting.
JavaScript Code
While following the steps above, use the following code in your JavaScript Expression:
{
let name = enter?.fieldname?.here ? enter?.fieldname?.here : '';
// Strip special characters
name = name.replace(/\!|\@|\#|\$|\%|\^|\&|\*|\(|\)|\_|\+|\'|\ʻ|\=|\:|\;|\<|\>|\?|\,|\.|\"|\|/g,"");
// Make text proper case and remove extra whitespace
function proper_case(str) {
let sentence = str.toLowerCase();
let separator = "";
if (sentence.search(" ") > -1) {
separator = " ";
sentence = sentence.split(separator);
sentence = sentence.filter(function (el) { return (el || el.length > 0); });
} else if (sentence.search("-") > -1) {
separator = "-";
sentence = sentence.split(separator);
sentence = sentence.filter(function (el) { return (el || el.length > 0); });
} else {
sentence = sentence;
}
if (separator === "") {
sentence = sentence.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + sentence.substr(1).toLowerCase();
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < sentence.length; i++) {
sentence[i] = sentence[i][0].toUpperCase() + sentence[i].substr(1).toLowerCase();
}
sentence = sentence.join(separator);
}
return sentence;
}
name = proper_case(name);
function replaceAccents(field) {
try {
if (field == null || typeof field == "undefined") {
return "";
}
} catch (e) {
return "";
}
// Replace accented characters
let noAccents = field.normalize("NFD").replace(/[\u0300-\u036f]/g, "")
.replace(/[ø]/g, "o")
.replace(/[Ø]/g, "O")
.replace(/[æ]/g, "ae")
.replace(/[Æ]/g, "Ae")
.replace(/[ə]/g, "e")
.replace(/[Œ]/g, "Oe")
.replace(/[œ]/g, "oe")
.replace(/[ß]/g, "ss")
.replace(/[§]/g, "S")
.replace(/[łı]/g, "l")
.replace(/[đ]/g, "d")
.replace(/[Đ]/g, "D")
.replace(/[þ]/g, "p");
return noAccents;
}
name = replaceAccents(name);
// Set character limit
return name.substring(0, 60);
}
Modify the Code
Once you've added this code to your JavaScript expression, you'll need to modify it. To do so:
- Indicate which field you want to modify. Each form in the software has a key associated with it. Each field within each form also has a key. Find the key for the specific field you want to export. Use that to replace enter?.fieldname?.here on the let name = line.
- Set the maximum number of characters you want to allow for this field. To do so, find the return proper_case(name).substring(0,60) line toward the end of the code. By default, the limit is 60 characters. To modify this limit, replace "60" with the number of your choice.
- After modifying the JavaScript Expression, click Update.
- If there are other fields you need to reformat, continue adding Calculated Fields and repeat the steps as described above. Then run your export.
Testing the Code
While building the export or your calculated property, click the Try It button to confirm that your variables are working.
Search for a record to complete your tests with. Confirm that the appropriate value appears in the Output window.
This article corresponds with JSO-163.